Diels Alder Reaction Between Two Rings
This reaction has a great synthetic importance and was discovered by two German chemists Otto Diels and Kurt Alder who received the 1950 Nobel Prize. The two double bonds in the central ring.
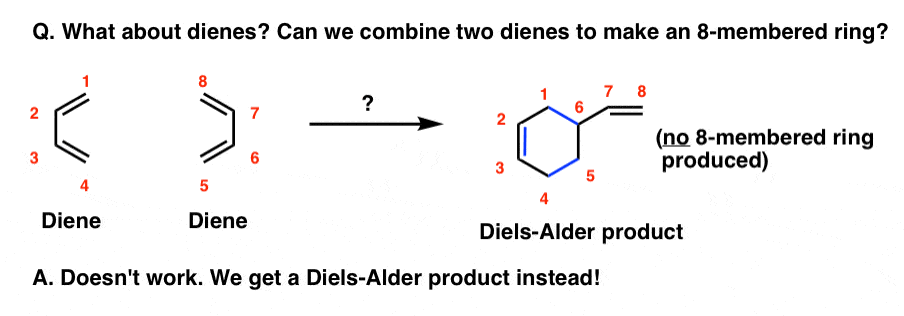
The Diels Alder Reaction Master Organic Chemistry
In organic chemistry the DielsAlder reaction is a chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene commonly termed the dienophile to form a substituted cyclohexene derivative.
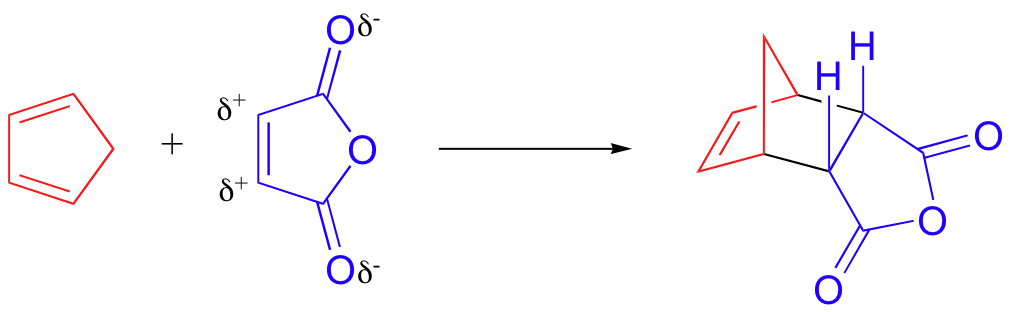
. The driving force of the reaction is the formation of new σ-bonds which are energetically more stable than the π-bonds. This is more favourable then the former example because both the very left as well as the very right ring of the product are in the state of a benzene ring each of these rings contain 6 π-electrons the prerequisite of a Hückel aromatic compound. 4 rows The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and.
A bicyclic ring system has two carbon rings that share common sides. Between Maleic anhydride and anthracene which is electron-rich and which is electron poor. The 42-cycloaddition of a conjugated diene and a dienophile an alkene or alkyne an electrocyclic reaction that involves the 4 π-electrons of the diene and 2 π-electrons of the dienophile.
In Diels-Alder reaction or Diels-Alder cycloaddition the atoms at the ends of the diene add to the dienophile double or triple bond alkene or alkyne thereby closing a ring product is cyclohexene. Conjugated dienes undergo a cycloaddition reaction with multiple bonds to form unsaturated six-membered rings. Since the reaction involves the formation of a cyclic product via a cyclic transition state it is also referred to as a cycloaddition.
When two cyclic structures combine in a Diels Alder reaction a third ring is formed in between the original ones. The DielsAlder reaction is the reaction between a conjugated diene and an alkene dienophile to form unsaturated six-membered rings. 1 The hetero-DielsAlder reaction is a variant of this reaction and is useful for the synthesis of six-membered heterocyclic rings.
The study of isolated atoms or molecules inside a fullerene cavity provides a unique environment. A typical Diels-Alder reaction happens via a concerted reaction with an aromatic which is so-called a transition state because it has six electrons that move cyclically and lower activation energy than expected otherwise as would be as in a benzene ring. At the same time three double bonds break while two single bonds form and a.
In organic chemistry the DielsAlder reaction is a chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene commonly termed the dienophile to form a substituted cyclohexene derivative. It was discovered by Otto Diels and Kurt Alder and both received a. 64 Compared to ligand 28 the ligand 29 with a dioxolane motif derived from.
Asymmetric DielsAlder reactions catalyzed by chiral titanium complexes has been reported. Essentially this process involves overlap of the 2p orbitals on carbons 1 and 4 of the diene with 2p orbitals on the two sp 2 -hybridized carbons of the dienophile. The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition of a 4 pi 2 pi diene dienophile system that forms a more stable product due to the fact that the sigma bonds created are more stable than the pi bonds destroyed.
Diels-Alder reactions are called 42 cycloadditions with the 4 indicates the reacting diene pi and the 2 indicates the. It is likely to control the outer carbon cage and study the isolated species when molecules or atoms are trapped inside a fullerene. If the solvent of a diels alder reaction is mesitylene rather than xylene what would happen to the reaction rate.
11ab Thus the complex prepared with TiCl 2 OPr i 2 and the TADDOL-type ligand 29 has been employed for the cycloaddition of simple dienes and αβ-unsaturated imides Scheme 19. These two outcomes are called exo and endo addition. It does not include even an intermediate it all happens in one step.
They were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1950. It is so much favourable to the former that this is. It is the prototypical example of a pericyclic reaction with a concerted mechanism.
The DielsAlder reaction is a well-known and established reaction in organic chemistry consisting of a highly selective 42 cycloaddition of a diene to an alkene dienophile to yield cyclohexene derivatives Scheme 28A. Since the reaction involves the formation of a cyclic product via a cyclic transition state it is also referred to as a cycloaddition. In conventional terminology this is a 14-addition of a diene and a dienophile.
Because the reaction is basically a concerted cyclization the diene must react in the cis conformation. An example of this stereospecificity is the reaction of 13butadiene with cisdiethylmaleate. This is a reaction between a diene and an olefin to give a new six-membered ring.
An exo addition looks something like this schematically. The DielsAlder reaction is the reaction between a conjugated diene and an alkene dienophile to form unsaturated six-membered rings. It is also termed a 4 2 cycloaddition because one partner the diene containing four π electrons adds to a two-electron fragment the olefin containing two π.
There are different ways the two original rings can combine leading to different stereochemical outcomes. This reaction has great synthetic importance and was discovered by two German chemists Otto Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928. More specifically it is classified as a thermally-allowed 2 cycloaddition with.
In a Diels-Alder reaction the alkene reacting partner is referred to as the dienophile. Comment on Connor Eksis post The. There are many of these processes but the most used and most useful is the DielsAlder reaction.
The DielsAlder reaction is an electrocyclic reaction which involves 42cycloaddition of 4 π-electrons of the. If the diene is a ring structure the DielsAlder reaction produces a bicyclic ring system. It is the prototypical example of a pericyclic reaction with a concerted mechanism.
The new bonds form simultaneously and stereospecifically. Alternatively a DielsAlder reaction with carbon atoms 9 and 10. In the Diels-Alder reaction a diene and dienophile react together to create a new six-membered ring.
The Diels-Alder reaction is the reaction of a diene with a dienophile to produce a cyclohexene ring. In the Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction a conjugated diene reacts with an alkene to form a ring structure. More specifically it is classified as a thermally-allowed 42 cycloaddition with.
What dienophile are we using. The DielsAlder reaction is an electrocyclic reaction which involves 42cycloaddition of 4 π-electrons of the. We report the DielsAlder addition reaction of 910-dimethyl anthracene DMA to H2C60 while 1H NMR spectroscopy is utilized to characterize.
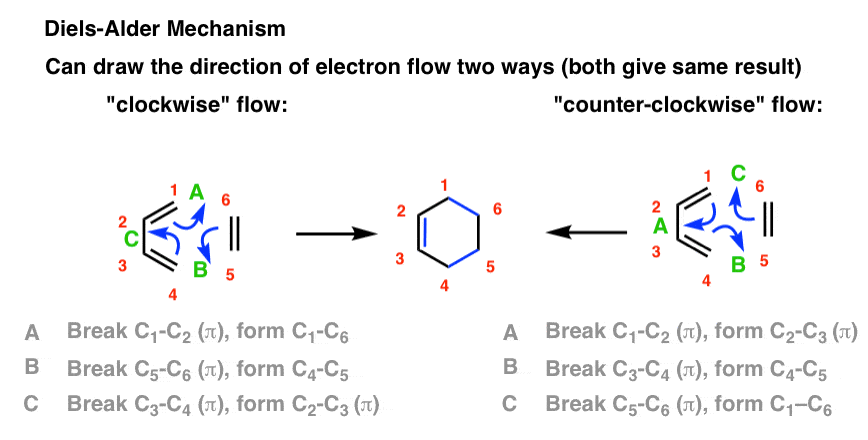
The Diels Alder Reaction Master Organic Chemistry
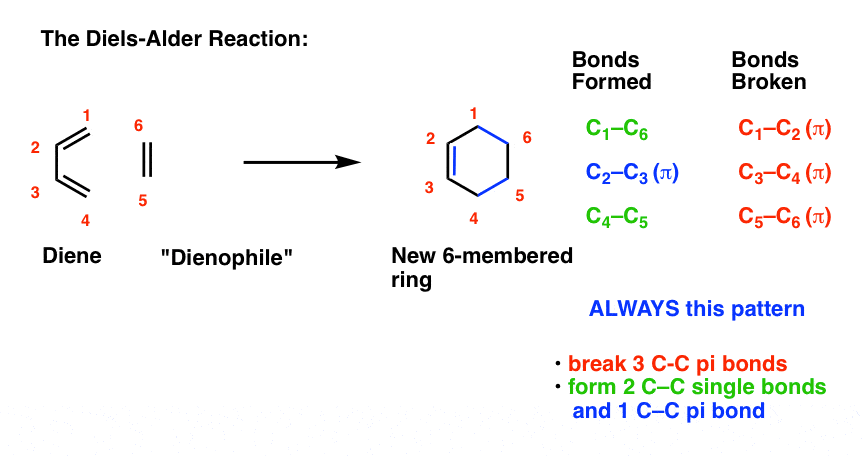
No comments for "Diels Alder Reaction Between Two Rings"
Post a Comment